
The equation above for Beta can also be re-arranged to make Ic as the subject, and with a zero base current ( Ib = 0 ) the resultant collector current Ic will also be zero, ( β x 0 ). The value of Beta for most standard NPN transistors can be found in the manufactures datasheets but generally range between 50 - 200. The values of Beta vary from about 20 for high current power transistors to well over 1000 for high frequency low power type bipolar transistors.
#NPN TRANSISTOR SYMBOL PLUS#
As the emitter current Ie is the product of a very small base current plus a very large collector current, the value of alpha α, is very close to unity, and for a typical low-power signal transistor this value ranges from about 0.950 to 0.999 Note that Beta has no units as it is a ratio.Īlso, the current gain of the transistor from the Collector terminal to the Emitter terminal, Ic/Ie, is called Alpha, ( α ), and is a function of the transistor itself (electrons diffusing across the junction). The value of β can be large up to 200 for standard transistors, and it is this large ratio between Ic and Ib that makes the NPN transistor a useful amplifying device when used in its active region as Ib provides the input and Ic provides the output. The transistor current in an NPN transistor is the ratio of these two currents ( Ic/Ib ), called the DC Current Gain of the device and is given the symbol of hfe or nowadays Beta, ( β ).
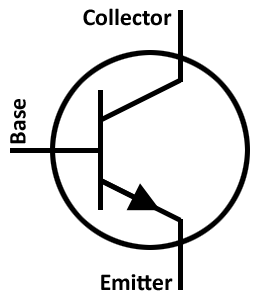
However, this only happens when a small biasing current ( Ib ) is flowing into the base terminal of the transistor at the same time thus allowing the Base to act as a sort of current control input. We know that the transistor is a "current" operated device (Beta model) and that a large current ( Ic ) flows freely through the device between the collector and the emitter terminals when the transistor is switched "fully-ON". The Base supply voltage V B is connected to the Base resistor R B, which again is used to limit the maximum Base current. The Collector is connected to the supply voltage V CC via the load resistor, RL which also acts to limit the maximum current flowing through the device. Then the voltage sources are connected to an NPN transistor as shown. So for an NPN transistor to conduct the Collector is always more positive with respect to both the Base and the Emitter. Also the Collector supply voltage is positive with respect to the Emitter ( V CE ).

The voltage between the Base and Emitter ( V BE ), is positive at the Base and negative at the Emitter because for an NPN transistor, the Base terminal is always positive with respect to the Emitter.
The construction and terminal voltages for an NPN transistor are shown above.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
